A handy A-Z guide to shooting terms
A useful dictionary of shooting terms

If you’re new to shooting you may find some of the terminology confusing. What do things like “ballistic co-efficient” mean and “drop at heel”? Read through our A-Z guide to shooting terms here and you’ll understand what a gunsmith is talking about and be able to hold your own in conversation with fellow shooters. In fact, your shooting vocabulary could even end up better than theirs …
While you’re at it, cast an eye over our useful pieces: “How a shotgun works” and “The anatomy of a shotgun“. Then you’ll be even better informed.
A
Accidental discharge Sometimes called a “negligent discharge”. It is the unintentional firing of a rifle or gun
Action The mechanism of a rifle or gun by which it is loaded, fired and unloaded
Airgun or Air Rifle A general term for any pistol or rifle that uses compressed air as a propellant. There are three main types of airgun: spring-powered, precharged pneumatic and CO2 powered. See below for more details. In England and Wales air rifles under 12ft.lbs. and air pistols under 6ft.bs. do not require a licence. In Scotland all airguns require a licence
B
BB A small ball bearing used in some types of airgun, (usually CO2 powered) or a size of shot in shotgun cartridges used for large game
Bag The term for shot quarry taken in a session out in the field
Ballistic co-efficient Measure of how streamlined a bullet is and how well it goes through the air
Barrel The hollowed out tube down which the ammunition is shot
Beaters A group of people who walk in a line with gun dogs ahead, driving the game forward out of cover
Bluing or blacking Protective coating on the metal parts of a rifle or shotgun with a distinctive blue/black colour
Bore Interior diameter of the barrel of a firearm, or calibre of a shotgun
Bore line An imaginary line from the muzzle of a gun along the centre of a barrel
Bolt Action A type of action that uses a manually-operated bolt to unload and load a gun. Bolt actions are usually found on rifles, but they can be used on small shotguns, such as a .410
Bullet A projectile fired from a rifle
Brace The term for a pair of shot quarry. So two pheasants would be a brace of pheasants and so on
Breech End of the barrel nearest the shooter where a bullet, cartridge or pellet is loaded

Beretta chokes
C
Cannelure A groove or indent around the base of a cartridge case where the extractor takes hold. Bullets also have cannelures to enable them to be crimped into the case
Carbon dioxide Sometimes used as a propellent for low-powered airguns
Cartridges These propel the shot towards the target. There are different types of cartridge for different quarry (clays, game and wildfowl) and the gun being used.
Cast The angle of the stock (left or right) to the centre line of the bore, which enables the shooter’s eye to line up, with the centre line of the bore
Centrefire A cartridge with a primer placed in the centre of the cartridge. This type of cartridge is suited to high power ammunition
Chamber length Chamber lengths in shotguns are usually 2½, 2¾ or 3 inch (65, 70 and 76mm). You will need to know the chamber length of your gun before buying cartridges – if you use the wrong size you can seriously injure yourself and damage your gun
Choke Chokes are fitted to gun barrels to restrict the width which has the effecting of ‘focusing’ the shot on the target
Clay or clay pigeon A disc thrown into the air and used as a target. Made from pitch and chalk, breaks when hit by shotgun pellets. Clays can be any colour but the weight and size is always consistent.
Close season Specific times of year when it is illegal to shoot different quarry, to allow them to move to new grazing grounds and produce young
Covert The area in which the quarry hides. A Covert can be woodland, hedgerows, crops (specific crops such as maize, kale or mustard can attract game and these are known as cover crops)

Driven shooting
D
Damascus barrels An early way of making barrels by welding strips of metal together around a rod and forge welding them together. This created a beautiful effect, but the barrels are not very strong
Decoy A dummy bird used to lure woodpigeons or geese within range of the shooter.
Dominant eye This is the stronger eye and is usually the eye a person would favour when looking down a telescope
Driven shooting The term for shooting when a line of beaters with dogs drive the game birds from their cover so they fly over the waiting Guns
Drop at heel, drop at comb, drop at toe These are measurements of how much the stock drops in certain places below the rib of the gun
Dry-firing Using an unloaded pistol or airgun to practice shooting techniques. Target shooters use it to build up muscle memory. Be warned, dry firing can damage the action on some firearms unless snap caps (see below) are used

Ejectors on a Benelli shotgun
E
Ear defenders These are vital to protect the shooter’s hearing when firing a shotgun or firearms
Ejector A mechanism that removes the cartridge from the breech of the gun after firing
Elevation The upward or downward adjustment of a sight
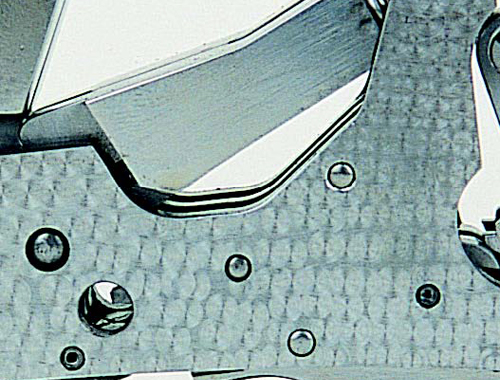
Engine turned rib All ‘engine turning’ means is ‘produced by machine’. Engine turning can produce many forms of pattern, from the coarse lines which might be used on a rib to a pattern of tiny, shiny circles. The coarse pattern is to prevent sun glare, while the tiny circle pattern allows retention of a very small amount of oil.
Etiquette Shooting has its own etiquette which is basically common sense and good manners. The form is different if you’re gameshooting or clayshooting. Always treat other Guns and your host as you would like to be treated yourself and you won’t go far wrong. You can read our extensive and informative articles on shooting etiquette which should cover everything you need to know – from what to wear to how to respond to a shooting invitation. In the meantime, here are the basic 10 commandments of shooting
- Always respond to a shoot invitation promptly whether you are planning to go or not
- Put your mobile phone away
- Dress appropriately for the day
- Tip the gamekeeper
- Listen carefully and attentively to the shoot briefing
- Follow the shooting safety rules to the letter
- Go to the peg you are assigned to – don’t hog the middle of the line
- Don’t boast or brag about your bag
- Don’t talk loudly when you’re on the peg and waiting for a drive and don’t bang your car door when you arrive
- Write a thank-you letter afterwards, particularly if you want to be invited back
Eye relief The distance between the shooter’s eye and the ocular lens (the lens nearest the eye) of the scope

Ferreting
F
Felt wad This separates the powder in the shotgun cartridge from the shot and pushes the shot down the barrel after the powder has ignited. Made from wood fibre, it is biodegradable unlike a plastic wad
Ferreting Ferrets are put down rabbit warrens to make the rabbits bolt outside into a waiting net. The rabbits are then shot immediately or dispatched humanely with a priest
Firearms certificate A licence needed to own firearms, or airguns over 12ft.lbs power.
Firing pin A small steel pin which strikes the metal primer of a cartridge to ignite the powder which then explodes pushing the bullet (rifle) or pellets (shotgun) out of the barrel
Fixed sights Sometimes called open sights, these are iron sights mounted on the rifle’s barrel
Flightline The path taken by birds in the sky to move between nests and feeding locations
Flinch A nervous twitch caused by firing a firearm and is often caused by the shooter fearing the recoil of a firearm. It can ruin accuracy
Ft.lbs The way the energy output of a rifle or airgun is measured
Full-bore Usually refers to rifles larger than .22 calibre that use centre- fire (see above) ammunition
Full metal jacket The copper covering of a lead bullet that allows the barrel to be driven up the barrel faster than a pure lead bullet

Group sizes
G
Group size The measurement of the patter of shots on a target for rifles and pistols
Gun The term for the individual shooting a gun out in the field. Always with a capital G
Gun fit The term used to fit a shotgun or rifle to an individual shooter’s body, so that the eye is aligned directly down the rib (shotgun) or scope (rifle). This produces much greater accuracy and usually minimizes the effect of recoil on the shooter
H
Hide Somewhere a shooter conceals themselves so they blend in with their surroundings

Shooting from a hide
L
Lamping Shooting predators pests after dark with a powerful lamp
Leading The ‘gunking up’ of the lands and grooves in a rifled barrel (see below) from bullets or airgun pellets. This can affect accuracy
Let-off The point at which the sears release the shot in a trigger mechanism. A crisp let-off means the trigger works rather like a switch and ‘creep’ refers to a more vague let-off point
Load The number of shot pellets packed into a cartridge. This is measured in grams and known as the ‘total weight’ of the shot. Recoil will be heavier with a high load
Load To put a cartridge into a firearm, or the composition of a cartridge
Lock, stock and barrel The three main parts of a shotgun. The lock refers to the action
Lock The mechanism that fires the gun when the trigger is pulled
Lock time The time taken from the release of the sear by the trigger to the moment the primer is struck. In airguns it refers to the time taken from the release of the sear to the exiting of the pellet from the barrel

Lamping
M
Magazine Part of a repeating rifle that stores ammunition ready for the next shot
Mildot This does not stand for “military” but refers to milliradian, which is a unitless measurement, similar to degrees
Mildot reticle A scope reticle designed around the measurement unit of a milliradian. This allows the shooter to calculate the distance of an object with known dimensions, helping range finding and accuracy
Minute of angle (MOA) Used by the military and target shooters and it is an angular measurement used as a reference for sight adjustment
Muzzle The end of a barrel
Muzzle energy The energy with which a projectile leaves the barrel, usually measured in ft.lbs.
Muzzle velocity The speed at which a bullet or pellet leaves the barrel

Gun muzzle
N
No-bird In clayshooting a referee will call this if either of the two targets breaks on leaving the trap, or in flight before a shot is taken. He will also call no bird if the clays flight path is clearly different to that of those thrown previously.

An over-and-under shotgun
O
Objective lens Lens of a telescopic sight nearest the object being viewed
Ocular lens Lens on a telescopic sight nearest the shooter’s eye
Over-and-under A shotgun where the barrels are placed one above the other
Open sights Non-telescopic sights, sometimes called iron sights
Over-travel The amount of movement on the trigger after the sear has been released

Proof marks
P
Parallax error This occurs when the target image does not fall in the same optical plane as the reticle. This affects all scopes, but many have a parallax adjuster that focuses the scope at one range and aids accuracy. With high magnification scopes parallax error is particularly acute
Peg Where the Gun stands waiting to take a shot at the quarry. Pegs are each given numbers and Guns draw at random from cards numbered accordingly. Hogging the middle peg is considered bad form and each Gun will move to a different peg at the end of a drive
Pellet A projectile made of lead used in an airgun, which is usually shaped like a shuttlecock. Sometimes called a slug
Picking-up It is the job of gundogs and their handlers to pick up fallen game and track down wounded birds (and dispatch them humanely).
Plinking A name given to informal target shooting with an airgun
Priest An instrument used for dispatching injured game humanely
Primer A small charge fitted in the centre of a centre fire cartridge or around the rim of a rim fire to ignite the main charge in a cartridge
Proof Process of checking that that a firearm is safe which is usually done by firing a special test cartridge which exceeds the guns tolerances by 30%
Proof mark The mark that proves the gun is safe and has passed proof (see above)

All shoots need a picking-up team
Q
Quarry This is your target of your shot – which may be a clay pigeon, a game bird, a rabbit, vermin or a deer.

Roughshooting
R
Recoil The rearward movement of a rifle or shotgun when it is fired
Reloading The process of refilling empty cartridge cases so they can be used again. This is done for economy and in the hope of increasing accuracy
Reticle The crosshairs on a telescopic sight
Rifle The barrels of this type of gun are rifled – marked with grooves which cause the bullet to spin, making it go further and hit more accurately. Rifles are used for killing quarry at a distance, cleanly and humanely. Ammunition is bullets and a firearms certificate (different from a shotgun licence) is required
Rough-shooting (see walked-up shooting)

A side-by-side shotgun
S
Semi-automatic A shotgun where cartridges are placed into a magazine which automatically loads the cartridges into the waiting chamber
Shot Shot pellets come in a variety of sizes from 2mm-8.4mm in diameter. They are usually made from lead (although steel shot is a legal requirement for wildfowling). The larger the shot, the fewer pellets in the cartridge. Large shot travels with more energy and goes further so it gives a clean kill for large or distant targets
So in shot size high numbers equal small shot – with 9 being the smallest, going to 1 and then into letters (BB and SG is the largest shot available used for hunting large animals and vermin)
Shotgun A shotgun has single or double barrels and fires shot contained in cartridges, which are place in the chamber of the gun
Shotgun certificate If you own a shotgun the law is that you need to be in possession of a valid shotgun certificate. You can however apply for the certificate before you buy a gun. Certificates are currently valid for five years and you should allow several months for a certificate to be granted. Here’s how to apply for a shotgun certificate
Side-by-side A shotgun where the barrels are literally placed side by side
Snapcap An inert cartridge used to release the tension on the firing pin spring of a shotgun or for dry-fire a rifle
Stalker Somebody who tracks deer in order to shoot particular animals
Stock The wooden, laminate or plastic part of the gun that rests against your shoulder
Struck-off Striking off is the final stage of shotgun barrel finishing, in which they are brought to an elegant taper and smoothed. Well struck-off barrels have a totally smooth and even finish. If the work has been done poorly marks will show through the blacking.

Trigger mechanism
Syndicate A group of shooters who combine forces and shoot together to share costs
T
Telescopic sight A sight which is rather like a telescope and magnifies the target
Tipping It is customary to tip the keeper at the end of the day, who will divide up tips amongst the beaters and pickers-up. As an old-fashioned rule, it’s £30 for the first 100 birds and then £10 for every 100 after that. However, if the Gun has had a particularly good day then generosity should prevail
Trap A device which throws up clay pigeons. It can be a legal machine to catch pests and predators.
Trigger blade Device operated by the shooter’s finger that operates the trigger system to fire the gun
Trigger mechanism The device that uses sears to release the firing pin of a firearm, or release the mechanism of an airgun to fire the shot
Twelve bore (or 16, 20, 28-bore) A gun bore is the dimeter of the barrel. A 28 bore is the smallest and a four bore the largest.

A fibre wad
W
Wad – packing that keeps the shot in position in the cartridge. Wad can be made from plastic, fibre or felt
Wad cutter A bullet or pellet with a flat nose used for target shooting because they produce neat holes on the target
Walked-up shooting. This is informal and consists of a handful of Guns, dogs and a gamekeeper. The group literally walk across fields and along hedges with the dogs going ahead, flushing out any game or rabbits around. This offers the hunters a challenging shot and the dogs then retrieve anything hit. The Guns have to have good reflexes and be able to make decisions quickly It is certainly a form of shooting that fully occupies the mind as the shooters have to be aware at all times of where everybody is and where the dogs are ranged. The small number of birds or rabbits shot are generally taken home to be cooked. In fact, this is shooting ‘living off the land’ and how many tenants used to feed their families back in the day
Alternatively walked-up shooting may be a form of pest control where corvids, rabbits and foxes are the quarry. Walked-up shooting can also be known as Rough shooting
Weight. Generally heavier guns absorb recoil better. A side-by-side is usually lighter than an over-and under
Windage The lateral adjustment of a sight

Young Shots (image via Schools Challenge)
Y
Young Shots. Shooting youngsters are collectively known as Young Shots – a term that usually covers them up until the age of 18

Zeroing your rifle can be done in any one of several ways
Z
Zero The range at which the point of aim and the point of impact coincide
Zoom A term that describes the magnification of a scope








